应用层
数据组织与传输
我们所写的提供网络服务的程序都是运行在应用层上的。在这些程序中,我们往往会使用结构体、类和对象等结构化的方式组织数据

但是在使用socket api接口时,我们只能使用字符串/字节流的格式来发送/接收信息,实现网络通信。但是对于提到的结构化数据,又该怎么使用网络通信传输呢?
应用层协议
针对应用层内的通信问题,我们依然使用协议解决。只要发送方和接收方按照同一’约定’对结构化数据进行字节流编码和字节流解析,就能够实现通过网络进行通信。这样的约定就是 协议。
既然协议是一种约定,那么就能开发出各种各样的的应用层协议。但它们往往会用到序列化和反序列化技术,所以我们先了解一下什么是序列化和反序列化
序列化与反序列化
这一技术能够在对象(结构化数据)和字节流之间架起桥梁,使对象能够更方便地支持网络通信,或者文件持久化。简单来说序列化就是基于某种规则把对象/结构化数据转化成字节流,反序列化就是基于同样的规则,把字节流还原成对象/结构化数据。

相关的序列化格式可以自己定义,当然也可以直接使用别人封装好的现成的格式。就比如常见的JSON,XML,YAML,Protobuf等,例子如下
JSON格式
1
2
3
4
| {
"name": "Tom",
"age": 23
}
|
XML格式
1
2
3
4
5
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<student>
<name>John Doe</name>
<age>21</age>
</student>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| student:
name: John Doe
age: 21
courses:
- Mathematics
- Physics
|
HTTP协议
HTTP协议也是大佬开发的非常好用,功能强大的应用层协议(不过不如HTTPS安全)。但是学习HTTP十分有助于我们学习网站的服务端是如何工作的。由此我们来展开介绍本篇文章的重点内容。
HTTP客户端-浏览器
根据前面的网络知识我们已经知道了一套网络系统一般是有客户端和服务端的。而我们HTTP服务的客户端就是现成的浏览器。现在浏览器功能已经十分强大了,尽管一般现在浏览器提供的是更安全的HTTPS通信服务,但是它依然兼容HTTP服务。所以我们直接使用现成的浏览器来测试我们后面编写的HTTP服务端即可
- 在使用
HTTP通信时:
- 总得来说浏览器的工作就是封装
HTTP报头并发送,以及接收来自服务器的HTTP响应,然后解析并渲染在界面上。
URL
URL是HTTP报头的重要组成部分,既然浏览器要跟服务端进程进行网络通信,当然得得知服务端进程的ip和端口号等信息,也就是在网络资源中的位置。确实我们可以在浏览器的地址栏里输入ip和端口号来访问我们的服务端进程,但URL的出现让我们有了更丰富的定位网络资源的方法。
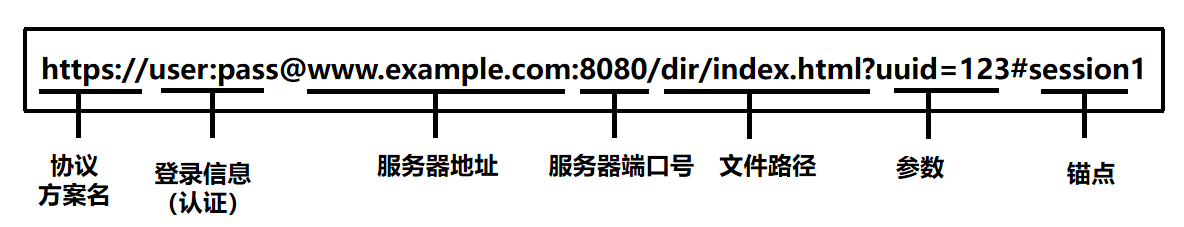
URL,Uniform Resource Locator, 统一资源定位符,通常包括如下部分
- 协议:如
http://、https://、ftp:// 等。
- 主机名或IP地址:如
www.example.com 或 192.168.0.1。
- 端口号(可选):如
:80、:443,如果是默认端口可以省略。
- 路径:标识具体资源的位置,如
/index.html。
- 查询参数(可选):如
?id=123&name=abc,用于传递参数。
- 锚点(可选):如
#section1,指向页面的某一部分。
URL encode和URL decode
在url的参数中可能需要表示像/,%这样的具有特殊含义的字符,或者是中文字符,这时候就需要根据URL encode编码规则对其进行转义,具体做法是将需要转码的字符转为16进制,然后从右到左,取4位(不足4位直接处理),每2位做一位,前面加上%,编码成%XY
如果我们要把它还原成原本的字符串,使用URL decode规则即可。
例子如下:

HTTP协议格式
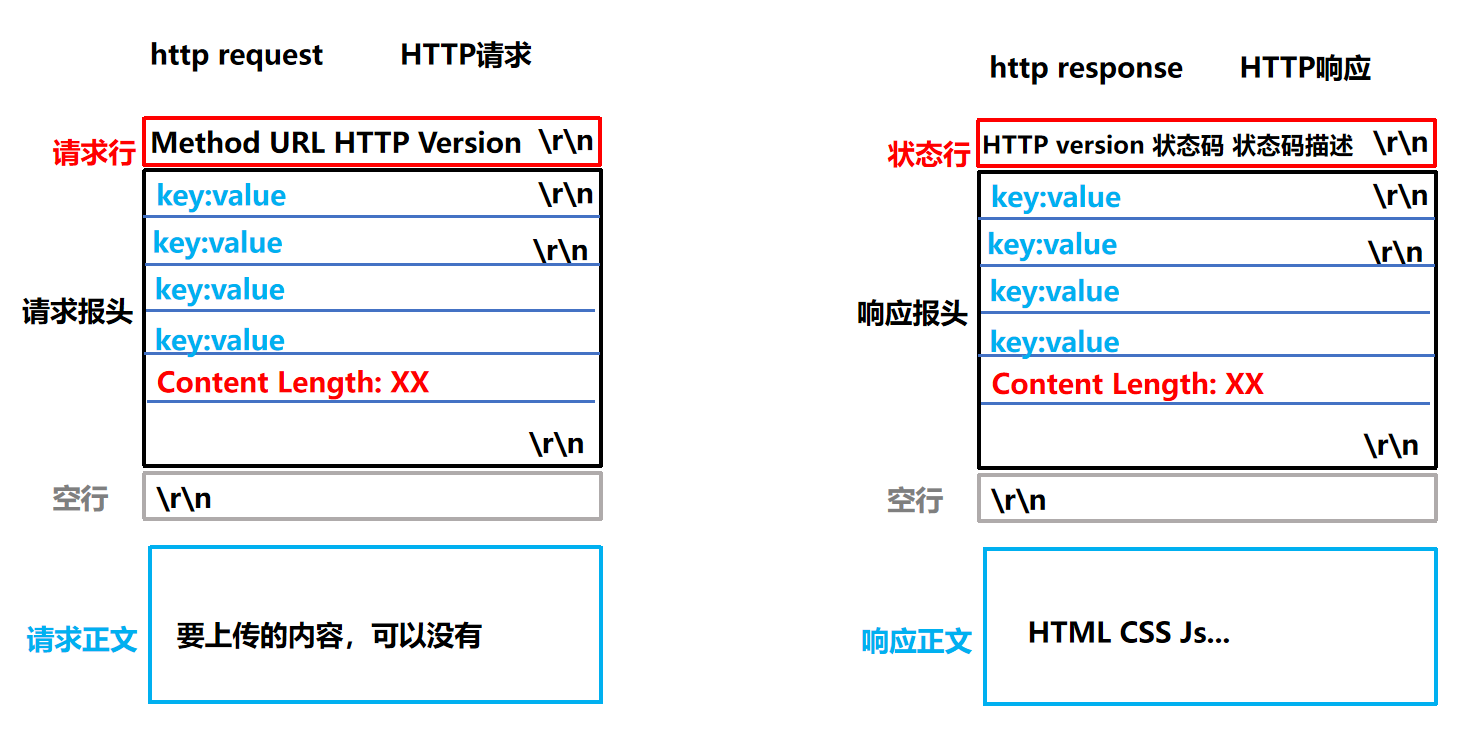
HTTP的请求和响应都遵循一定的格式要求:
- HTTP请求
- 首行:
方法+URL+协议版本
- Header:求的属性,冒号分割的键值对;每组属性之间使用\n分隔;遇到空行表示Header部分结束
- Body:行后面的内容都是Body.Body允许为空字符串.如果Body存在,则在Header中会有一个Content-Length属性来标识Body的长度
- HTTP响应
- 首行:
版本号+ 状态码+ 状态码解释
- Header:同上
- Body:同上
其中的URL我们已经介绍过了,协议版本也不作介绍,我们接下来介绍一下方法和状态码
HTTP的方法
HTTP的方法决定了浏览器通知服务器如何响应以及响应的内容,同时也决定了浏览器将调用哪些接口接收响应
| 方法 |
说明 |
支持的HTTP协议版本 |
| GET |
获取资源 |
1.0、1.1 |
| POST |
传输实体主体 |
1.0、1.1 |
| PUT |
传输文件 |
1.0、1.1 |
| HEAD |
获得报文首部 |
1.0、1.1 |
| DELETE |
删除文件 |
1.0、1.1 |
| OPTIONS |
询问支持的方法 |
1.1 |
| TRACE |
追踪路径 |
1.1 |
| CONNECT |
要求用隧道协议连接代理 |
1.1 |
| LINK |
建立和资源之间的联系 |
1.0 |
| UNLINK |
断开连接关系 |
1.0 |
其中最常用的就是GET方法和POST方法.
HTTP状态码
状态码更多的是属于前后端的一种约定,怎么发和怎么处理取决于程序员,浏览器默认并不会根据状态码有什么响应。
| 状态码 | 类别 | 原因短语 |
| 1XX | Informational(信息性状态码) | 接收的请求正在处理 |
| 2XX | Success(成功状态码) | 请求正常处理完毕 |
| 3XX | Rediection(重定向状态码) | 需要进行附加操作以完成请求 |
| 4XX | Client Error(客户端错误状态码) | 服务器无法处理请求 |
| 5XX | Server Error(服务器错误状态码)| 服务器处理请求出错 |
Content-Type: 数据类型(text/html等)Content-Length: Body的长度Host: 客户端告知服务器, 所请求的资源是在哪个主机的哪个端口上;User-Agent: 声明用户的操作系统和浏览器版本信息;referer: 当前页面是从哪个页面跳转过来的;location: 搭配3xx状态码使用, 告诉客户端接下来要去哪里访问;Cookie: 用于在客户端存储少量信息. 通常用于实现会话(session)的功能;
代码实践:获取HTTP请求并发送响应
这边先用一下之前博客实现的简易日志器和封装好的套接字类,这里不赘述
log.hpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
| #pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define LOG_FILE "log.txt"
#define SIZE 1024
enum OUT_MODE
{
Screen,
OneFile,
MultiFile
};
enum LEVEL
{
Info,
Debug,
Warning,
Error,
Fatal
};
class Log
{
public:
Log(OUT_MODE om = Screen):_om(om)
{}
~Log(){}
void enable(OUT_MODE om)
{
_om = om;
}
std::string levelToString(LEVEL level)
{
switch (level)
{
case Info:return "Info";
case Debug:return "Debug";
case Warning:return "Warning";
case Error:return "Error";
case Fatal:return "Fatal";
default: return "None";
}
}
void logmessage(LEVEL level,const char *format,...)
{
char leftBuffer[SIZE] = {0};
time_t t = time(nullptr);
struct tm *ctime = localtime(&t);
snprintf(leftBuffer,sizeof(leftBuffer),"[%s][%d-%d-%d %d:%d:%d]",levelToString(level).c_str(),1900+ctime->tm_year,1+ctime->tm_mon,ctime->tm_mday,
ctime->tm_hour,ctime->tm_min,ctime->tm_sec);
va_list s;
va_start(s,format);
char rightBuffer[SIZE];
vsnprintf(rightBuffer,sizeof(rightBuffer),format,s);
va_end(s);
char logtxt[SIZE*2];
snprintf(logtxt,sizeof(logtxt),"%s %s",leftBuffer,rightBuffer);
printLog(level,logtxt);;
}
void operator()(LEVEL level,const char *format,...)
{
char leftBuffer[SIZE] = {0};
time_t t = time(nullptr);
struct tm *ctime = localtime(&t);
snprintf(leftBuffer,sizeof(leftBuffer),"[%s][%d-%d-%d %d:%d:%d]",levelToString(level).c_str(),1900+ctime->tm_year,1+ctime->tm_mon,ctime->tm_mday,
ctime->tm_hour,ctime->tm_min,ctime->tm_sec);
va_list s;
va_start(s,format);
char rightBuffer[SIZE];
vsnprintf(rightBuffer,sizeof(rightBuffer),format,s);
va_end(s);
char logtxt[SIZE*2];
snprintf(logtxt,sizeof(logtxt),"%s %s",leftBuffer,rightBuffer);
printLog(level,logtxt);;
}
void printLog(LEVEL level, const std::string& logtxt)
{
switch(_om)
{
case Screen:std::cout<<logtxt<<std::endl;break;
case OneFile:printOneFile(LOG_FILE,logtxt);break;
case MultiFile:printMultiFile(level,logtxt);break;
default: break;
}
}
void printOneFile(const std::string& logname,const std::string& logtxt)
{
int fd = open(logname.c_str(), O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_APPEND,0666);
if(fd<0) return;
write(fd,logtxt.c_str(),logtxt.size());
close(fd);
}
void printMultiFile(LEVEL level,const std::string logtxt)
{
std::string filename = LOG_FILE;
filename+= ".";
filename += levelToString(level);
printOneFile(filename,logtxt);
}
private:
OUT_MODE _om = Screen;
};
Log log;
|
Socket.hpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
| #pragma once
#include <unistd.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include "log.hpp"
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <string>
enum{
SOCK_ERR = 2
,BIND_ERR
,LISTEN_ERR
,ACCEPT_ERR
};
const int backlog = 10;
extern Log log;
class Sock
{
public:
Sock(){}
~Sock(){}
public:
void Socket()
{
_sockfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
if(_sockfd < 0)
{
log(Fatal,"socket error,errno: %d error string:%s",errno,strerror(errno));
exit(SOCK_ERR);
}
int opt = 1;
setsockopt(_sockfd,SOL_SOCKET,SO_REUSEADDR,&opt,sizeof(opt));
}
void Bind(uint16_t port)
{
struct sockaddr_in local;
memset(&local,0,sizeof(local));
local.sin_family = AF_INET;
local.sin_port = htons(port);
local.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
if(bind(_sockfd,(const struct sockaddr*)&local,sizeof(local)) < 0)
{
log(Fatal,"bind error,errno: %d error string:%s",errno,strerror(errno));
exit(BIND_ERR);
}
}
void Listen()
{
if(listen(_sockfd,backlog) < 0)
{
log(Fatal,"listen error,errno: %d error string:%s",errno,strerror(errno));
exit(LISTEN_ERR);
}
}
int Accept(std::string* clientip,uint16_t* clienport)
{
struct sockaddr_in peer;
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
int newfd = accept(_sockfd,(struct sockaddr*)&peer,&len);
if(newfd < 0)
{
log(Fatal,"accept error,errno: %d error string:%s",errno,strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
char ipstr[64] = {0};
inet_ntop(AF_INET,&peer.sin_addr,ipstr,sizeof(ipstr));
*clientip = ipstr;
*clienport = ntohs(peer.sin_port);
return newfd;
}
bool Connect(const std::string& ip,uint16_t port)
{
struct sockaddr_in peer;
memset(&peer,0,sizeof(peer));
peer.sin_family =AF_INET;
peer.sin_port = htons(port);
inet_pton(AF_INET,ip.c_str(),&(peer.sin_addr));
int n = connect(_sockfd,(struct sockaddr*)&peer,sizeof(peer));
if(n == -1)
{
std::cerr<<"connect to "<<ip<<":"<<port<<std::endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
void Close()
{
close(_sockfd);
}
int Fd()
{
return _sockfd;
}
private:
int _sockfd;
};
|
我们重点介绍如何把HTTP服务器相关的代码封装进HttpServer.hpp中
头文件包含和全局变量设置如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| #pragma once
#include "log.hpp"
#include "Socket.hpp"
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
#include <unordered_map>
const std::string wwwroot = "./wwwroot";
const std::string sep = "\r\n";
const std::string homepage = "/index.html";
const uint16_t default_port = 25565;
class HttpServer;
|
接下来我们封装一个HttpRequest用于处理HTTP请求
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
| struct ThreadData
{
ThreadData(int fd, HttpServer *svr)
: sockfd(fd), httpsvr(svr)
{
}
int sockfd;
HttpServer *httpsvr;
};
class HttpRequest
{
public:
void Deserialize(std::string req)
{
while (true)
{
std::size_t pos = req.find(sep);
if (pos == std::string::npos)
break;
std::string temp = req.substr(0, pos);
if (pos == 0)
break;
req_header.push_back(temp);
req.erase(0, pos + sep.size());
}
text = req;
}
void Parse()
{
std::stringstream ss(req_header[0]);
ss >> _method >> _url >> _http_version;
_res_path = wwwroot;
if(_url == "/" || _url == "index.html")_res_path+= homepage;
else _res_path += _url;
auto pos = _res_path.find(".");
if(pos == std::string::npos) _suffix = ".html";
else _suffix = _res_path.substr(pos);
}
void DebugPrint()
{
std::cout << "\n----------------------------\n";
for (auto &line : req_header)
{
std::cout << line << "\n\n";
}
std::cout << "----------------------------\n";
std::cout<<text<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"methond: "<<_method<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"url: "<<_url<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"http version: "<<_http_version<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"resource path: "<<_res_path<<std::endl;
}
public:
std::vector<std::string> req_header;
std::string text;
std::string _method;
std::string _url;
std::string _http_version;
std::string _res_path;
std::string _suffix;
};
|
可以看到我们把完整的HTTP请求交给HttpRequest后它会自动分离部首Header和Body,以及提取方法,URL,协议版本,资源路径和后缀信息
特别的,我们对响应做如下组装(序号表示行顺序)
"HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n"或者"HTTP/1.0 404 Bad\r\n""Content-Length: " + to:string(text.size())std::string blockline = "\r\n"std::string text
接下来我们实现HttpServer类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
| class HttpServer
{
public:
HttpServer(uint16_t port = default_port)
: _port(port)
{
_content_type.insert({".html","text/html"});
_content_type.insert({".png","image/html"});
_content_type.insert({".jpg","image/jpeg"});
}
~HttpServer() {}
bool Start()
{
_listen_sock.Socket();
_listen_sock.Bind(_port);
_listen_sock.Listen();
log(Info, "Server started running");
for (;;)
{
std::string clientip;
uint16_t clientport;
int sockfd = _listen_sock.Accept(&clientip, &clientport);
std::cout<<"\n";
log(Info, "get a new link [%s:%u] sockfd:%d", clientip.c_str(), clientport, sockfd);
pthread_t tid;
ThreadData *td = new ThreadData(sockfd, this);
pthread_create(&tid, nullptr, ThreadRun, td);
}
}
static void *ThreadRun(void *args)
{
pthread_detach(pthread_self());
ThreadData *td = static_cast<ThreadData *>(args);
HandlerHttp(td->sockfd, td->httpsvr);
delete td;
return nullptr;
}
static std::string ReadHtmlContent(const std::string &htmlpath)
{
std::ifstream in(htmlpath,std::ios::binary);
if (!in.is_open())
return "";
in.seekg(0,std::ios::end);
auto len = in.tellg();
in.seekg(0,std::ios::beg);
std::string content;
content.resize(len);
in.read((char*)content.c_str(),content.size());
in.close();
return content;
}
std::string Suffix2Desc(const std::string& suffix)
{
auto iter = _content_type.find(suffix);
if(iter == _content_type.end()) return _content_type[".html"];
else return _content_type[suffix];
}
static void HandlerHttp(int sockfd, HttpServer *httpsvr)
{
char buffer[10240];
ssize_t n = recv(sockfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1, 0);
if (n > 0)
{
buffer[n] = 0;
std::cout << buffer;
HttpRequest req;
req.Deserialize(buffer);
req.Parse();
std::string path = req._res_path;
bool ok = true;
std::string text = ReadHtmlContent(path);
if(text.empty())
{
std::string err_html = wwwroot;
err_html+="/";
err_html+="err404.html";
text = ReadHtmlContent(err_html);
ok=false;
}
std::string response_line;
if(ok)
response_line = "HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n";
else
response_line = "HTTP/1.0 404 Bad\r\n";
std::string response_header = "Content-Length: ";
response_header += std::to_string(text.size());
response_header += "\r\n";
response_header += httpsvr->Suffix2Desc(req._suffix);
response_header += "\r\n";
response_header+="Set-Cookie: name=supdriver";
response_header += "\r\n";
response_header+="Set-Cookie: password=password";
response_header += "\r\n";
response_header+="Set-Cookie: view=./a/b/hello.html";
response_header += "\r\n";
std::string block_line = "\r\n";
std::string response = response_line;
response += response_header;
response += block_line;
response += text;
send(sockfd, response.c_str(), response.size(), 0);
}
close(sockfd);
}
private:
Sock _listen_sock;
uint16_t _port;
std::unordered_map<std::string,std::string> _content_type;
};
|
然后我们简单地给index.html和err404.html添加点内容
index.html
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>test</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 style="background-color: aqua;"><a href="./a/b/hello.html" style="text-decoration: none;">Hello world</a></h1>
<h1 style="background-color: aqua;">你好,世界</h1>
<h1 style="background-color: aqua;">你好,世界</h1>
<h1 style="background-color: aqua;">你好,世界</h1>
<form action = "/a/b/hello.html" method=get> <!-- get是通过url提交参数的 -->
<label>(get)Name:
<input name="submitted-name" autocomplete="name" />
</label>
<button type="submit">Save</button>
</form>
<div style="margin-top:2em;">
<form action = "/a/b/hello.html" method=post style="background-color: antiquewhite;"> <!-- get是通过url提交参数的 -->
<label>(post)Name:
<input name="submitted-name" autocomplete="name" />
</label>
<button type="submit">Save</button>
</form>
</div>
<div class="myimgs" style="height: 400px;display: flex;">
<div style="display: flex;width: 50%;justify-content: center;">
<img src="./img/p1.jpg" alt="图片1">
</div>
<div style="display: flex;width: 50%;justify-content: center;">
<img src="./img/p2.jpg" alt="图片2" >
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
err404.html
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div style="margin: auto;">
<h1 style="font-size: 200px;text-align: center;">404 not found</h1>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
最后我们再写一个.cpp源文件用于执行main()函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| #include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include "HttpServer.hpp"
extern Log log;
int main()
{
std::unique_ptr<HttpServer> svr(new HttpServer());
svr->Start();
return 0;
}
|
然后我们编译并运行可执行程序,在自己的浏览器上输入对应的URL

可以看到我们的浏览器成功渲染出了首页(index.html)的信息

同时服务端也打印出了HTTP请求报头






